CALCANEAL APOPHYSITIS / SEVERS
What is Calcaneal Apophysitis?
Calcaneal apophysitis, previously commonly known as Sever's (disease), is a frequent cause of heel pain in growing children and adolescents. This condition results from inflammation of the growth plate in the heel, typically affecting active children between the ages of 8 and 14. Sever's disease is not actually a disease but rather an overuse injury caused by repetitive stress on the heel, hence why the moniker has been replaced by its anatomically correct name.
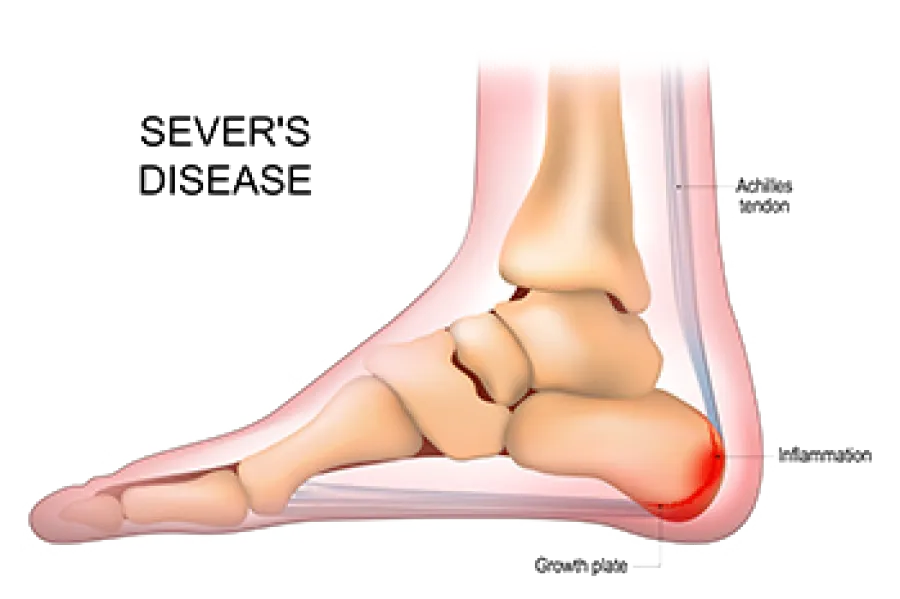
Causes of Calcaneal Apophysitis
Several factors contribute to the development of Sever's disease, including:
1. Growth Spurts:
Rapid growth periods can cause the heel bone to grow faster than the surrounding muscles and tendons, leading to increased tension and stress.
2. Physical Activity:
High-impact activities, such as running, jumping, and sports that involve repetitive heel striking, can aggravate the growth plate.
3. Poor Footwear:
Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or cushioning can exacerbate the condition.
4. Foot Mechanics:
Flat feet, high arches, or an abnormal gait can place additional strain on the heel.
Symptoms of Calcaneal Apophysitis
Common symptoms include:
Heel Pain
Pain at the back or bottom of the heel, which usually worsens with activity and improves with rest.
Tenderness
The heel may be tender to the touch.
Swelling
Some children may experience swelling or redness in the heel.
Limping
Due to pain, the child may limp or walk on their toes to avoid putting pressure on the heel.
Stiffness
Stiffness in the heel, especially after exercising or first thing in the morning.
Diagnosing Calcaneal Apophysitis
A podiatrist or pediatrician can diagnose Sever's through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests like X-rays or Ultrasound to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment strategies for calcaneal apophysitis include:
Rest and Activity Modification:
Limiting or avoiding activities that cause heel pain is crucial for recovery.
Orthotic Devices:
Custom orthotics may be recommended to improve foot mechanics and provide additional support.
Proper Footwear:
Ensuring the child wears supportive and cushioned shoes can alleviate pressure on the heel.
Stretching Exercises:
Gentle stretching exercises for the calf muscles and Achilles tendon can help relieve tension on the heel.
Ice Therapy:
Applying ice packs to the heel can help reduce inflammation and pain.
NSAIDs:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy:
A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen and stretch the affected area.
Heel Cups or Cushions:
Using heel cups or cushioned insoles can provide extra padding and support.
Preventing Calcaneal Apophysitis
To prevent Sever's disease, consider these strategies:

Gradual Increase in Activity:
Gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activities to avoid overloading the heel.

Supportive Footwear:
Wearing well-cushioned and supportive shoes, particularly during high-impact activities, helps reduce stress on the heel in growing children.
Stretching and Strengthening:
Encourage regular stretching and strengthening exercises for the calf muscles and Achilles tendon.

Cross-Training:
Incorporate low-impact activities like swimming or cycling to reduce repetitive stress on the heel.

Monitor Growth Spurts:
Monitoring periods of rapid growth and moderating physical activity can help prevent excessive strain on the heel.
When to Consult a Podiatrist
Persistent heel pain, swelling, or difficulty with regular activities in children should be evaluated by a podiatrist to prevent further complications.
SERVICING BRISBANE'S WESTERN SUBURBS
Neat Feet Podiatry Care
Marshall Lane Health Clinic
8 Marshall Lane, Kenmore QLD 4069
Monday - Closed
Tuesday 9am - 5pm
Wednesday 8am - 4pm
Thursday 10am - 6pm
Friday 9am - 5pm

